Complex tables made easy
Introduction
DataTables is a very powerful javascript library for creating tables with complex user interactions. It has dozens of configuration options and can be quite complicated to set up correctly. The Yada Framework implements a Java Fluent API that produces the required javascript configuration and provides the needed backend functionality for server-side data loading.
The current implementation covers all the core DataTables options and the Responsive extension.
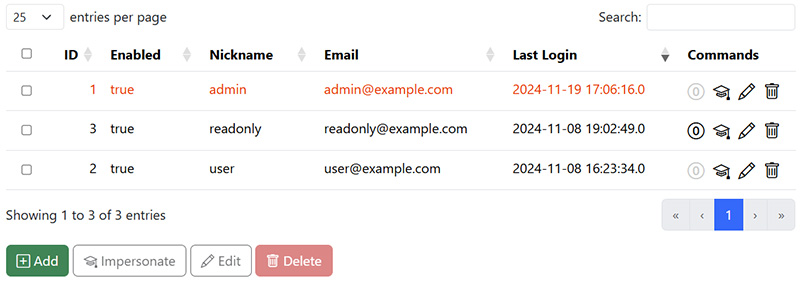
| A full example is implemented in the YadaExamples project. |
Prerequisites
The DataTables library can either be downloaded locally or from a CDN. In both cases the official download page offers different options to package the required elements into a downloadable zip or a specific CDN url for javascript and CSS. The Yada Framework implementation has been tested with:
Styling framework |
Bootstrap 5 |
|---|---|
Packages |
DataTables |
Extensions |
Responsive |
This example is for a downloaded version:
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" th:href="@{/static/datatables-2.1.8/datatables.min.css}"/>
</head>
...
<script th:src="@{/static/datatables-2.1.8/datatables.min.js}"></script>The yada.datatables.js file also needs to be loaded. This is by default automatically
packaged in the war distribution for production but should be added in development:
<script th:if="${@config.developmentEnvironment}" th:src="@{/yadares/js/yada.datatables.js}"></script>HTML Code
The basic DataTable functionality is implemented just by adding the yada:datatable tag:
<yada:datatable (1)
yada:configuration="${userTableAttribute}"> (2)
</yada:datatable>| 1 | The tag inserts the table at the specified position in the HTML |
| 2 | The configuration must have been set in the @Controller as a Model attribute, called "userTableAttribute" in this example |
For advanced scenarios where you need to alter the configuration before
creating the table or work with the created table in javascript, two handlers
can be provided via yada:preprocessor and yada:postprocessor:
<yada:datatable
yada:configuration="${userTableAttribute}"
yada:preprocessor="userTablePreprocessor" (1)
yada:postprocessor="userTablePostprocessor"> (2)
</yada:datatable>| 1 | The preprocessor can alter the configuration before the table is created |
| 2 | The postprocessor can operate on the table once it has been created |
More details below.
Java Fluent Interface
The configuration for a DataTable is implemented in a YadaDataTable instance.
This instance should be added to the Model with an attribute that must have the same name
used in yada:configuration, e.g. userTableAttribute in the example above.
YadaDataTable myDataTable = ...
model.addAttribute("userTableAttribute", myDataTable);The instance is a singleton identified by a unique id and is produced by yadaDataTableFactory.
This ensures that the table configuration code is run only once for all HTTP requests
and that the same configuration can be used in the ajax handler that loads the table data.
To create or get an instance the syntax is as follows:
YadaDataTable myDataTable = yadaDataTableFactory.getSingleton("myTableId", locale, ...);The locale is needed to load the i18n file and can be omitted or set to null to use the default locale that is either set in the application XML configuration or taken from the platform. In a multilanguage application it should be taken from a parameter in the @Controller @RequestMapping.
The table configuration is added as a lambda after the locale parameter and uses the fluent iterface:
YadaDataTable yadaDataTable = yadaDataTableFactory.getSingleton("userTable", locale, table -> {
table
.dtAjaxUrl("someUrl")
.dt...
});| Using the lambda ensures that the configuration code is run just once. |
All methods of the fluent interface have the "dt" prefix. This makes IDE suggestions more focused on the useful methods during autocompletion:
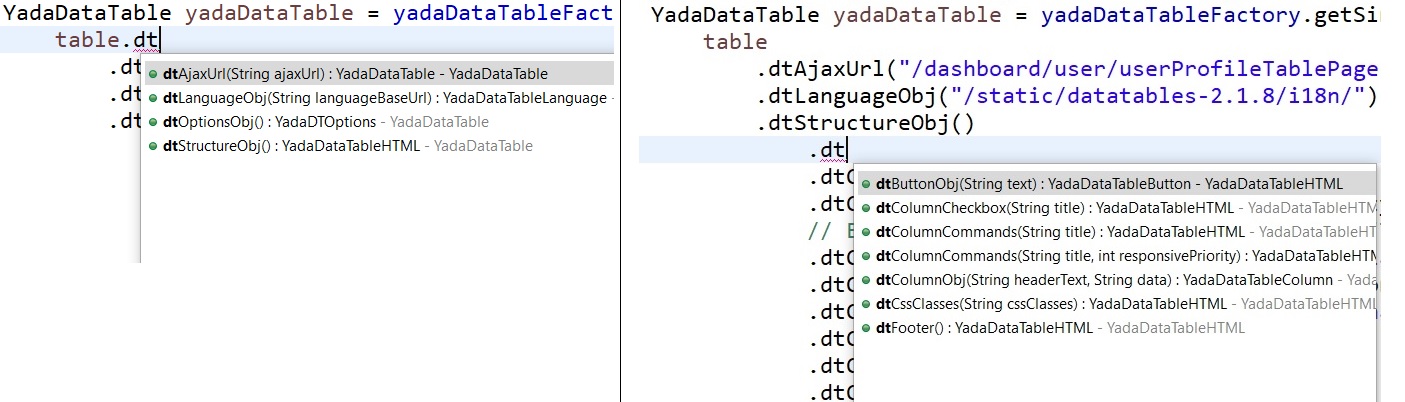
When a configuration option has many parameters, the corresponding
method name has the "Obj" suffix because a new object is returned to provide the new
configuration methods.
To "exit" from the current object, the back() method must be called.
Basic Configuration
The most basic table configuration, that can be used to show data taken from an @Entity, only requires the entity class and fields:
@RequestMapping("/user")
public String users(Model model) {
YadaDataTable basicTable = yadaDataTableFactory.getSingleton("basicTable", table -> {
table
.dtEntityClass(UserProfile.class) (1)
.dtStructureObj()
.dtColumnObj("Email", "userCredentials.username").back() (2)
.dtColumnObj("Last Login", "userCredentials.lastSuccessfulLogin").back() (2)
.back();
});
model.addAttribute("basicTable", basicTable);
return "/dashboard/users";
}| 1 | Provide the class of the entity that holds data |
| 2 | Provide the column names and the path of the properties that hold the value to show |
On the page the table is shown with:
<yada:datatable
yada:configuration="${basicTable}">
</yada:datatable>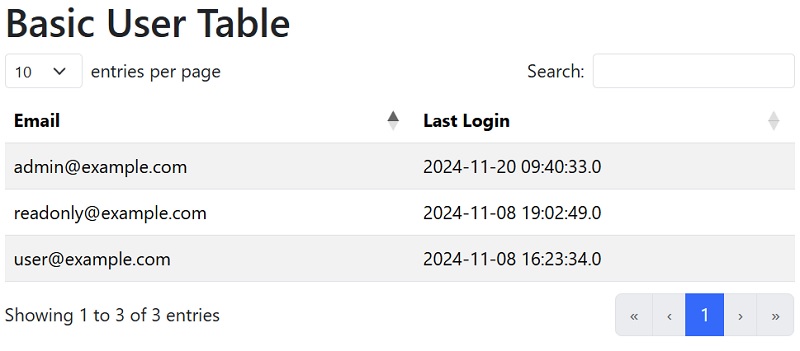
the endpoint is implemented in YadaController.yadaDataTableData()
|
Data retrieval will be automatic and will have the same security restrictions of the page where the table is shown, which is "/dashboard/user" in the example.
| security is implemented in SecurityConfig if the application is secured |
Advanced Configuration
In more advanced scenarios the ajax endpoint returning data can be customized with dtAjaxUrl().
This is an alternative approach to dtEntityClass() and using both will result in error.
The argument of dtAjaxUrl() is either the url for the ajax call that retrieves data
from the backend or a method reference to it. The string parameter can contain any Thymeleaf expression and will be included
in a standard URL expression like @{/myUrl} when not already provided.
The dtStructureObj() top method starts configuration of the "structure" of the table using a custom API that can be explored with autocompletion. This API allows the definition of columns and buttons.
The other top method is .dtOptionsObj() that allows access to the official
DataTables options. For example, the PageLength
option can be set with .dtOptionsObj().dtPageLength(25).
All the DataTables core options and the Responsive extension options are available
unless they are deprecated or not applicable in the context of the Yada Framework,
like retrieve.
| anything that can’t be done in Java can be done in javascript using pre- and post- processors. |
YadaDataTable yadaDataTable = yadaDataTableFactory.getSingleton("userTable", locale, table -> {
table
.dtEntityClass(UserProfile.class)
.dtAjaxUrl(this::userProfileTablePage)
.dtLanguageObj("/static/datatables-2.1.8/i18n/") (1)
.dsAddLanguage("pt", "pt-PT.json") (2)
.back()
.dtStructureObj()
.dtCssClasses("yadaNoLoader") (3)
.dtColumnObj("ID", "id")
.dtResponsivePriority(80) (4)
.back()
.dtColumnObj("column.enabled", "userCredentials.enabled") (5)
.dtResponsivePriority(40)
.back()
.dtColumnObj("Title", "title."+locale.getLanguage()) (6)
.back()
.dtColumnObj("Email", "userCredentials.username")
.dtName("userCredentials.username") (7)
.dtOrderAsc(0) (8)
.back()
.dtColumnObj("Last Login", "userCredentials.lastSuccessfulLogin")
.dtOrderDesc(1) (9)
.dtCssClasses("nowrap") (10)
.back()
.dtColumnCheckbox("select.allnone") (11)
.dtColumnCommands("column.commands", 10) (12)
.dtButtonObj("Disabled") (13)
.dtUrl("@{/dashboard/user/dummy}") (14)
.dtIcon("<i class='bi bi-0-circle'></i>") (15)
.dtShowCommandIcon("disableCommandIcon") (16)
.back()
.dtButtonObj("button.add")
.dtUrl("@{/dashboard/userwrite/ajaxEditUserProfileForm}")
.dtGlobal() (17)
.dtIcon("<i class='bi bi-plus-square'></i>")
.dtToolbarCssClass("btn-success") (18)
.dtRole("ADMIN") (19)
.back()
.dtButtonObj("button.impersonate")
.dtUrlProvider("impersonate") (20)
.dtNoAjax() (21)
.dtIcon("<i class='bi bi-mortarboard'></i>")
.dtRole("ADMIN").dtRole("supervisor")
.back()
.dtButtonObj("button.edit")
.dtUrl("@{/dashboard/userwrite/ajaxEditUserProfileForm}")
.dtElementLoader("#userTable") (22)
.dtIcon("<i class='bi bi-pencil'></i>")
.dtIdName("userProfileId") (23)
.dtRole("ADMIN")
.back()
.dtButtonObj("button.delete")
.dtUrl("@{/dashboard/userwrite/ajaxDeleteUserProfile}")
.dtIcon("<i class='bi bi-trash'></i>")
.dtRole("ADMIN")
.dtMultiRow() (24)
.dtToolbarCssClass("btn-danger")
.dtConfirmDialogObj() (25)
.dtTitle("Delete User")
.dtMessageSingular("usertable.delete.confirm.singular")
.dtMessagePlural("usertable.delete.confirm.plural")
.dtConfirmButton("button.confirm").dtAbortButton("modal.confirm.cancel")
.dtPlaceholderColumnName("userCredentials.username")
.back()
.back()
.dtFooter() (26)
.back()
.dtOptionsObj() (27)
.dtResponsiveObj() (28)
.dtDetailsObj()
.dtDisplay("DataTable.Responsive.display.childRowImmediate")
.back()
.back()
.dtPageLength(10) (29)
.dtColumnDefsObj() (30)
.dtTargetsName("userCredentials.username")
.dtAriaTitle("This is the user email")
.back()
.dtColumnDefsObj()
.dtTargetsName("userCredentials.lastSuccessfulLogin")
.dtAriaTitle("usertable.aria.lastlogin")
.back()
.back()
;
});| 1 | Set the base url where language files are located. It can be the official DataTables URL or a local endpoint. By default the "it", "de", "es" and "fr" languages are loaded. |
| 2 | Add a language definition that is not loaded by default. |
| 3 | CSS classes to set on the <table> tag |
| 4 | Control the order in which columns are hidden when the page is resized |
| 5 | Add a new column to the table. Order is preserved. |
| 6 | The column value can be a localized text |
| 7 | Set a name on this column for database operations and cross references, e.g. with column definitions |
| 8 | Set the column as the first default sort column, ascending |
| 9 | Set the column as the second default sort column, descending |
| 10 | CSS classes to set on the cell |
| 11 | Adds the leftmost column with checkboxes to select rows |
| 12 | Adds a rightmost column with buttons for each row |
| 13 | Adds a button called "Disabled" to the toolbar |
| 14 | URL to be called when the button is clicked |
| 15 | Icon to be displayed on the button |
| 16 | Javascript function to be called to decide wether the icon on the row must be shown |
| 17 | The button is "global", i.e. is shown in the toolbar, not in the row, and is always enabled |
| 18 | CSS class to be added to the button in the toolbar |
| 19 | The button is shown only to users with the "ADMIN" role. Can be called may times with different role values |
| 20 | The URL is provided by a javascript function |
| 21 | The click does not perform an ajax call, it just follows the link |
| 22 | Specify a CSS selector for an element that should be covered with a "loader" icon while the ajax call is in progress |
| 23 | Name of the ID request parameter sent in the call, default is "id". Useless for global buttons |
| 24 | Enable the toolbar button when one or many rows are selected. The default is for the toolbar button to be enabled only when one row is selected |
| 25 | Enable javascript-side confirmation dialog for button action |
| 26 | Adds a footer to the table showing the same content as the header |
| 27 | Start configuration of the "options" of the DataTable. See the official DataTables documentation for details |
| 28 | Enable the Responsive extension |
| 29 | Number of rows to show per page |
| 30 | Configure column definitions: a way to set column options after a column has been defined |
Java Ajax Endpoint
The Yada Framework implementation of DataTables assumes that data is fetched via ajax from the server, therefore the ajax option is forced to be active.
The ajax endpoint is set via .dtAjaxUrl() on the YadaDataTable object as explained before. The
@Controller should query the database, performing searching and sorting, and return a JSON
file with the resulting data for the current page.
When the table shows data from @Entity objects, most of that code is already provided.
@RequestMapping(value ="/user/userProfileTablePage", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) (1)
@ResponseBody public Map<String, Object> userProfileTablePage(YadaDatatablesRequest yadaDatatablesRequest, Locale locale) { (2)
Map<String, Object> result = yadaDataTableDao.getConvertedJsonPage(yadaDatatablesRequest, UserProfile.class, locale); (3)
return result; (4)
}| 1 | Any type of mapping can be used, not just @RequestMapping |
| 2 | YadaDatatablesRequest is initialized with the metadata sent by DataTables, like the current page number, the value paths and the search/sort options |
| 3 | yadaDataTableDao.getConvertedJsonPage() receives the request data and the @Entity class to perform all needed operations |
| 4 | The result is a "map tree" (i.e. nested maps) that is automatically converted to json |
Using a custom endpoint for table data allows to manipulate both the query and the result, for example by adding conditions or creating values not directly found on the entity:
Advanced Usage
DataTables API Access
A reference to the DataTables API, i.e. the object returned by $table.DataTable(dataTableOptions), is added to the table DOM object under the yadaDataTableApi key. It can be retrieved with
const dataTableApi = $('#yourTableId').data('yadaDataTableApi');All standard DataTable API methods are available, for example use dataTableApi.ajax.reload() to reload the table data.
Table Filter
You can add form elements to filter the data shown in your DataTable.
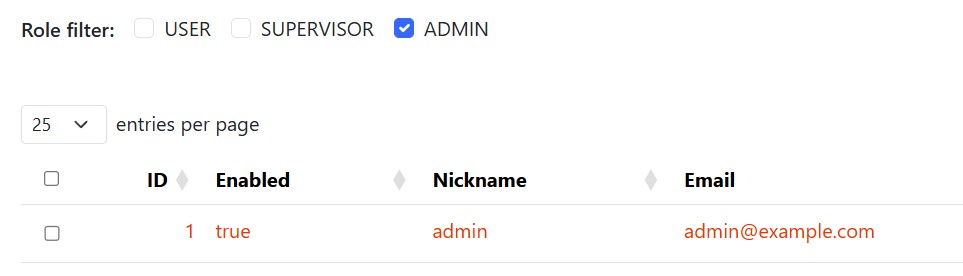
On the HTML page create a form with the CSS class yada_dataTables_{tableId} where {tableId} is the ID of your table: any input fields, checkboxes, or select elements in this form will automatically be sent to the server when the table loads or refreshes.
On the backend, the form data is available in the YadaDatatablesRequest object passed to the ajax endpoint. You can access the form data using the getExtraParam() method, which returns a Map<String, String> containing the form field names and values.
The sql used by yadaDataTableDao.getConvertedJsonPage() to read table data can be customized by adding conditions to the YadaSql object returned by yadaDatatablesRequest.getYadaSql().
For example, if you have a table showing users, you can add checkboxes to filter by user role, or text inputs to search by name. When users interact with these form elements, call dataTableApi.ajax.reload() to refresh the table with the new filter values.
See YadaExamples/src/main/java/net/yadaframework/example/web/dashboard/UserProfileController.java for a full example.
Returning extra data
The call to yadaDataTableDao.getConvertedJsonPage() returns all data that was requested, but sometimes some other attributes
may be required to compute a row value. In order to retrieve this data, use yadaDatatablesRequest.addExtraJsonAttribute("attributePath") before calling getConvertedJsonPage().
A use case could be to fetch the "enabled" attribute of the user credentials to show a different icon based on that value.
Dynamic row CSS from the backend
The backend can set a specific CSS class on each row by implementing a getDT_RowClass() method on the entity. The method must return the class name to be added to the row:
@Transient
@JsonProperty("DT_RowClass")
public String getDT_RowClass() {
// Set a specific class on admins
if (hasAnyRoleKey("ADMIN")) {
return "userProfileAdmin";
}
return null;
}row class from the backend reference pre- and post- processors examples i18n is automatic by using keys instead of words