Quickly assembling forms with advanced functionality
Description
Creating a form often implies adding a lot of code to make input fields more user-friendly, like showing validation messages, adding help and sort buttons, implement value suggestions, etc. The Yada Framework offers some reusable code in the form of Thymeleaf includes and custom dialect tags.
Thymeleaf Includes
General Syntax
The net.yadaframework.views.yada.form package inside /YadaWeb/src/main/resources contains some
HTML files that can be included in the Thymeleaf templates with the standard syntax:
<div th:replace="~{/yada/form/text::body(fieldName='subject',maxlength=64,required=true,labelKey='form.label.subject')}"></div>Parameters can be specified, as usual, either on the replace directive itself or by creating variables on some parent element using th:with.
|
Some of these components are being replaced by custom dialect tags to offer an easier syntax. |
Available Fragments
- boolean
-
A checkbox for boolean elements
- checklist
-
A checkbox list for objects, maps or static (Spring-EL) elements
- enum
-
A select list for enums
- fileUpload
-
A file-upload input element
- list
-
A select list for objects, maps or static (Spring-EL) elements
- radio-values
-
A radio list for static (Spring-EL) elements
- range
-
A range numeric input with label and value display
- text
-
A text input element
A detailed syntax of the usage can be found in the source of each fragment.
Entity Sorter: allows to add, edit and sort a set of database @Entity objects link to file upload page explain all
Thymeleaf Yada Dialect
Introduction
The Yada Dialect is a custom Thymeleaf Dialect that adds Yada functionality generally already available with some other syntax (e.g. template fragments or data- attributes) but makes the source code more readable. Some tags implement form components.
link to generic introduction to the yada dialect
<yada:input>
The <yada:input> purpose is to eventually replace the text fragment, but it currently implements some
different functionality:
-
numeric fields show increment/decrement buttons
-
a bootstrap "addon" can be set right and left of the field
-
password fields have a "show" button
-
a help button can be added
-
can control the value of the character counter
<yada:inputCounter> -
show a dropdown with input suggestions
|
|
All attributes that are normally available on a HTML <input> tag can also be used,
including all Yada ajax directives.
Example of a numeric input field with increment/decrement buttons that submits its value via ajax when it changes:
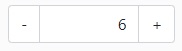
<yada:input type="number" min="0" max="99"
yada:ajax="@{/setRooms(annuncioId=${annuncio.id})}"
class="yadaNoLoader"> (1)
</yada:input>| 1 | The yadaNoLoader class is added to hide the loader on the ajax call |
Note: ajax submission also works on plain <input> tags using the yada:ajax attribute.
Example of a numeric input field that shows trailing zeroes without increment/decrement buttons:

<yada:input name="price" type="number" min="0"
class="noButtons"> (1)
<yada:addonRight>.00</yada:addonRight> (2)
</yada:input>| 1 | The noButtons class is added in order to hide the unneeded buttons with some custom CSS: |
| 2 | bootstrap addon |
.yadaInput.noButtons {
.yadaInputNumericDecrement, .yadaInputNumericIncrement, .yadaShowPasswordAddon {
display: none;
}
}A boostrap addon can be set either right or left of the input
field with the addonLeft and addonRight tags, that accept valid HTML:
<yada:input name="price">
<yada:addonLeft><b>$</b></yada:addonLeft>
<yada:addonRight>.00</yada:addonRight>
</yada:input>When the input tag is of type="file", the standard behavior is extended so that the chosen file can also
be removed via a specific trash icon that appears after file selection.

<yada:input type="file" id="someFileUpload">
<yada:addonRight>
<i class="bi bi-upload" onclick="$('#someFileUpload').click();"></i> (1)
</yada:addonRight>
</yada:input>| 1 | This optional addon is for the upload icon shown in the above image |
The tag works perfectly with type="radio" inputs, but when the possible radio values come from an Enum a single
tag can show all choices:

<yada:input type="radio" name="color" th:value="${product.color}"
yada:enumclassname="com.example.ColorEnum" (1)
yada:labelKeyPrefix="enum.campaignType." (2)
yada:ajax="@{/setColor(productId=${product.id})}">
</yada:input>| 1 | The yada:enumclassname attribute specifies the Enum where values have to be taken |
| 2 | The yada:labelKeyPrefix attribute specifies the key in message.properties for the label:
the enum value is appended to the prefix in order to derive the key |
|
The tag is implemented in |
Suggestion list
The <yada:input> tag can be used to implement a dropdown that shows a list of suggestions as the user
types some characters. It needs a backend @RequestMapping that receives the field value and returns
the HTML of the dropdown.
The usage scenario is that the user types some characters in the input field and sees some suggestions; he can either choose one of the suggestions or keep typing until an "end-of-input" character is typed. The text (or text and id) is then sent to the backend that will add a new element and return an HTML showing all elements so far added. This HTML will be inserted in page.
Input tag example:
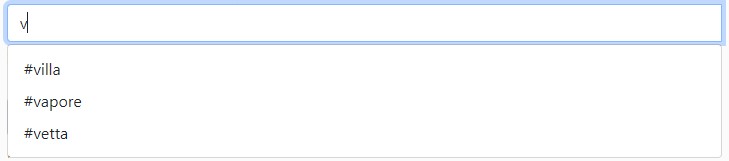
<yada:input name="dogname"
yada:ajax="@{/addDog(ownerId=${owner.id})}" (1)
yada:updateOnSuccess="'yadaParents:.jsDogsSection'"> (2)
<yada:suggestion
yada:listUrl="@{/dognameSuggestion}" (3)
yada:suggestionRequestIdNameOverride="dogId"> (4)
</yada:suggestion>
</yada:input>| 1 | ajax URL called when the user chooses a value from the suggestion list or types an "end-of-input" character
like Enter, Space, Comma etc. (see yada.suggestionList in yada.dialect.js for details) |
| 2 | selector that identifies the portion of the page that has to be replaced with the result of the ajax call |
| 3 | ajax URL called to retrieve the HTML of the suggestions |
| 4 | when the optional yada:suggestionRequestIdNameOverride is specified, this is the name of the request parameter
that contains the id of the element chosen from the suggestion list (see below) when sending the chosen value via ajax |
The backend code for the listURL can return any HTML with a <ul class="dropdown-menu wide jsYadaSuggestionList">
element that contains '<a>' elements. The anchors text is used as the value for the field. The anchors
data-id attribute is sent to the backend when present.
A ready-made HTML for this is implemented in /YadaWeb/src/main/resources/net/yadaframework/views/yada/formfields/inputSuggestionFragment.html
and can be used by adding a model attribute named yadaSuggestions with a value of either a "value List" or a
"value-id Map", and returning YadaViews.AJAX_SUGGESTION_FRAGMENT:
@RequestMapping("/dognameSuggestion")
public String dognameSuggestion(String prefix, Model model, Locale locale) {
List<String> suggestions = getDognameSuggestions(prefix, locale); // Some DB query
model.addAttribute("yadaSuggestions", suggestions);
return YadaViews.AJAX_SUGGESTION_FRAGMENT;
}The above example is the simplest case where just the text of the chosen suggestion is sent to the
backend when calling the addURL. The name of the request parameter will be the same as the name
of the input field, or "value" if no name has been specified.
When a Map is used, choosing a suggestion will send the map key as the "id" request parameter and the map value
as the value of the input field.
The name of the "id" parameter can be overridden with the addIdRequestNameOverride attribute as
seen above: this has precedence over anything else (see YadaInputTagSuggestion interface below).
@RequestMapping("/dognameSuggestion")
public String dognameSuggestion(String prefix, Model model, Locale locale) {
List<Dog> suggestions = getDogs(prefix, locale); // Some DB query that returns Dog objects
// Convert the list to a map
Map<Long, String> idToValue = suggestions.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Dog::getId, Dog::getName));
model.addAttribute("yadaSuggestions", idToValue);
return YadaViews.AJAX_SUGGESTION_FRAGMENT;
}|
For more advanced use cases or when you don’t want to convert a list of objects to a Map,
those objects can implement the You can then return computed values for the text and the id, and rename the
request parameter for the id by implementing the |
Backend code for the addURL that receives the dogname field and any other
parameters set on the URL (ownerId in this example:
@RequestMapping("/addDog")
public String addDog(String dogname, Long ownerId, Model model, Locale locale) {
List<String> allDogs = addDog(ownerID, dogname);; // Some code to add the name of the dog to its owner
model.addAttribute("allDogs", allDogs);
return "/fragments/dogList :: fragment";
}|
The tag is implemented in |
Ajax and Validation Messages
When using ajax to handle input field submissions, the standard th:errors tags and BindingResult
techniques won’t work unless returning the whole form (but th:field on yada:input currently
doesn’t work).
Other than implementing your custom solution, you can use either the yada:validationError attribute
or the <yada:validationError> tag:
<yada:input name="dogname" yada:validationError="${dogNameError}"When the value of yada:validationError is not blank, its value is shown as an error below the input tag
using Bootstrap 5 classes for styling. This is the quickest solution.
When you need more control on the error appearance, you can use the <yada:validationError> tag instead:
<yada:input name="dogname"
...
<yada:validationError yada:invalidFlag="${dognameHasError}" th:text="#{error.dogname}">
(Dummy) error text here
</yada:validationError>
Using the tag syntax, an error is shown when the value of yada:invalidFlag is neither null
nor false. In the above example the error is shown with
model.addAttribute("dognameHasError", true);
// Also:
model.addAttribute("dognameHasError", "yes");The error message can either be the static text inside the tag, or any th:text value. In the
above example, a localized text is being fetched from message.properties.
The tag syntax also accepts a MessageSource key:
<yada:input name="dogname"
...
<yada:validationError yada:messageKey="${dognameErrorKey}">
Localized error text example
</yada:validationError>model.addAttribute("dognameErrorKey", "error.dogname.short");
// or
model.addAttribute("dognameErrorKey", "error.dogname.long");The error is visible only if ${dognameErrorKey} is not null.
The yada:invalidFlag attribute is optional when yada:messageKey is used.
<yada:inputCounter>
The <yada:inputCounter> purpose is to show a character counter when the user types in
a <yada:input> text field.
It can be placed anywhere in the HTML but must have a unique id that must be referenced from
the yada:inputCounterId attribute of the <yada:input> tag.
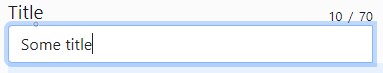
<yada:inputCounter id="titleCounter"></yada:inputCounter>
<yada:input yada:inputCounterId="titleCounter" name="title" maxlength="70"></yada:input>The label to the left of the counter isn’t added automatically: it can be set with a container div with appropriate CSS:
<div class="labelAndCounter">
<label for="title">Title</label>
<yada:inputCounter id="titleCounter"></yada:inputCounter>
</div>
<yada:input yada:inputCounterId="titleCounter" name="title" maxlength="70"></yada:input>.labelAndCounter {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}|
The tag is implemented in |
<yada:textarea>
The <yada:textarea> tag produces a standard <textarea> HTML tag but can also use some of
the features available to the <yada:input> tag.
Currently only the `<yada:inputCounter>` tag has been implemented and tested with `<yada:textarea>`, while other features like addons and validation have been copied over from the input tag but never tested.
The value of a <textarea> can normally be implemented with a th:text attribute but this currently doesn’t
work, so the yada:text attribute should be used instead for this specific purpose.
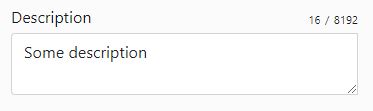
<yada:inputCounter id="descriptionCounter"></yada:inputCounter>
<yada:textarea id="description" name="description"
yada:text="*{description}" (1)
yada:inputCounterId="descriptionCounter" (2)
maxlength="8192"> (3)
</yada:textarea>| 1 | The value of the textarea is set with yada:text |
| 2 | A counter can be used |
| 3 | The length must be set in order to use the counter |
The label to the left of the counter isn’t added automatically: it can be set
with a container div as shown above for the <yada:input> tag.
|
The tag is implemented in |